Documentation added 4 February 2021 by Vikram K. Mulligan, Flatiron Institute (vmulligan@flatironinstitute.org).
Application purpose
The trRosetta application uses the trRosetta neural network described in Yang et al. (2020) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117(3):1496-1503 (doi 10.1073/pnas.1914677117) to generate inter-residue distance and orientation constraints for a sequence of unknown structure given a multiple sequence alignment. The application then uses the Rosetta minimizer to find the backbone conformation consistent with the constraints. This allows faster and more accurate structure prediction than the classic AbintioRelax application. This reproduces the Python protocol described in Yang et al., but offers advantages in speed and disk usage, automatic job distribution via the Rosetta job distributor, and a few additional options.
Compilation requirements
The trRosetta application requires that Rosetta be linked against the Tensorflow C-API libraries. To compile with Tensorflow support:
-
Download the Tensorflow 1.15 precompiled libraries for your operating system from one of the following. (Note that GPU versions require CUDA drivers; see https://www.tensorflow.org/install/lang_c for more information.)
- Linux/CPU: https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/libtensorflow/libtensorflow-cpu-linux-x86_64-1.15.0.tar.gz
- Linux/GPU: https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/libtensorflow/libtensorflow-gpu-linux-x86_64-1.15.0.tar.gz
- Windows/CPU: https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/libtensorflow/libtensorflow-cpu-windows-x86_64-1.15.0.zip
- Windows/GPU: https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/libtensorflow/libtensorflow-gpu-windows-x86_64-1.15.0.zip
- MacOS/CPU: https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/libtensorflow/libtensorflow-cpu-darwin-x86_64-1.15.0.tar.gz
- MacOS/GPU: None available.
-
Unzip/untar the archive into a suitable directory (~/mydir/ is used here as an example), and add the following environment variables:
- Linux, Windows:
- LIBRARY_PATH=$LIBRARY_PATH:~/mydir/lib
- LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:~/mydir/lib
- MacOS:
- LIBRARY_PATH=$LIBRARY_PATH:~/mydir/lib
- DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH=$DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH:~/mydir/lib
- Linux, Windows:
Edit your user.settings file (Rosetta/main/source/tools/build/user.settings), and uncomment (i.e. remove the octothorp from the start of) the following lines:
import os 'program_path' : os.environ['PATH'].split(':'), 'ENV' : os.environ,Compile Rosetta, appending extras=tensorflow (for CPU-only) or extras=tensorflow_gpu (for GPU) to your scons command. For example:
./scons.py -j 8 mode=release extras=tensorflow bin
Note that the 'ENV' line in the user.settings file should be in the "override" section. If this has been moved to another section, you may get a KeyError:'LESS' error on compilation.
A note on nomenclature
Although "omega" and "phi" are commonly used to refer to the third and first mainchain backbone dihedrals of an alpha amino acid, and "theta" is used to refer to the second mainchain backbone dihedral of a beta-amino acid, in the context of trRosetta-related protocols, these Greek letters are assigned new meanings. Here, "omega" refers to the inter-residue dihedral angle between the CA and CB atoms of a first residue and the CB and CA atoms of a second residue. "Theta" refers to the inter-residue dihedral angle between the N, CA, and CB atoms of a first residue and the CB atom of a second residue. And "phi" refers to the inter-residue angle between the CA and CB atoms of a first residue and the CB atom of a second residue.
trRosetta algorithm
The trRosetta application takes two inputs: a sequence (in FASTA format) and a multiple sequence alignment (in .a3m format). Multiple sequence alignments can be generated using the HHBlits webserver (https://toolkit.tuebingen.mpg.de/tools/hhblits); for an example of an MSA in .a3m format, see the trRosettaProtocolMover documentation. The trRosetta application then carries out the following steps:
The multiple sequence alignment is converted to a one-hot 3D tensor (sequence position x sequence x amino acid identity), which is provided to the trRosetta neural network.
The trRosetta neural network runs, applying a series of 2D convolutional layers to transform the inputs into a set of output tensors. These include 3D inter-residue distance probability distribution tensor (res1 x res2 x binned inter-residue distances), two 3D inter-residue torsion probability tensors for the inter-residue dihedrals omega and theta (see note above), and a 3D inter-residue angle probability distributoin for the inter-residue angle phi (see note above).
-
A centroid-mode representation of the sequence is built, and its initial conformation is randomized. Randomization modes include:
- The "classic" protocol of Yang et al. For each amino acid residue, backbone phi and psi dihedral angles are set randomly to one of (-140, 153), (-72, 145), (-122, 117), (-82, -14), (-61, -41), or (57, 39), with probailities weighted to favour likely secondary structures. No considreation is given to the amino acid conformational preferences of different amino acid types, and all backbone omega angles are set to 180 degrees (i.e. cis peptide bonds are not sampled). This protocol is default.
- The "ramachandran" protocol. Each amino acid's phi and psi dihedrals are drawn from the probability distribution for that amino acid using the RandomizeBBByRamaPrePro mover. Residues preceding prolines use different distributions (i.e. the rama_prepro energy function's probability distributions are used). Cis peptide bonds are sampled with low probability (default is 0.05% of the time) except at pre-proline positions, where they are sampled with moderate probability (default is 5% of the time, to match PDB statistics).
- The "bins" protocol. The backbone conformation is initialized using the InitializeByBins mover, which sets the conformation of each pair of amino acids by choosing backbone conformational bins based on PDB statistics listing the probability of seeing residue i in bin X and residue i+1 in bin Y. Exact backbone phi and psi values are drawn from the Ramachandran distribution within each bin, and cis amide bonds are sampled in proportion to PDB statistics. See the documentation for that mover for details.
The trRosettaConstraintGenerator is used to conver the inter-residue distance, omega, theta, and phi distributions into atom pair, dihedral, dihedral, and angle constraints, respectively.
-
The MinMover is used to pull the backbone from its initial, random conformation into a conformation that is consistent with the constraints. Regardless the minimization protocol, minimization involves alternating rounds of torsion-space and Cartesian-space minimization, with an energy function that blends the centroid scoring function with constraint penalty terms. Available minimization protocols include:
- The "classic0" protocol, which first minimizes using only short-range constraints, then minimizes using short+intermediate-range constraints, then minimizes using all constraints.
- The "classic1" protocol, which first minimizes using short+intermediate-range constraints, then minimizes using all constraints.
- The "classic2" protocol, which immediately minimizes using all constraints. This protocol is default.
The pose is converted to an all-atom model.
The FastRelax protocol is applied with constraints present, and torsion/Cartesian space minimization alternating with the "dualspace" protocol of Conway et al. (2014) Protein Sci 23(1):47-55 (doi 10.1002/pro.2389). This refines backbone and side-chain geometry.
A final pose is written to disk. Statistics such as RMSD to native (after Centroid and fullatom refinement phases) and execution time are included.
Options
Option | Setting |Type| Description
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| | |
in:file: | | |
fasta | | (F)| Fasta-formatted sequence file
native | | F| Native PDB filename
in:detect_disulfides | | B| If true, detects potential
| | | disulfides after centroid phase
| | | (default true)
| | |
trRosetta: | | |
msa_file | | F| Filename for a multiple
| | | sequence alignment file,
| | | in a3m format. Dashes
| | | indicate gap sequences,
| | | and lowercase characters
| | | will be removed (and
| | | flanking regions ligated).
use_distance_constraints | | B| Should distance constraints
| | | generated by the trRosetta
| | | neural network be used
| | | during structure
| | | prediction? Default true.
use_omega_constraints | | B| Should omega dihedral
| | | constraints generated by
| | | the trRosetta neural
| | | network be used during
| | | structure prediction?
| | | Note that this is NOT the
| | | backbone omega dihedral
| | | angle, but an
| | | inter-residue dihedral
| | | defined by
| | | CA1-CB1-CB2-CA2. Default
| | | true.
use_theta_constraints | | B| Should theta dihedral
| | | constraints generated by
| | | the trRosetta neural
| | | network be used during
| | | structure prediction?
| | | Note that this is an
| | | inter-residue dihedral
| | | defined by N1-CA1-CB1-CB2.
| | | Default true.
use_phi_constraints | | B| Should phi angle constraints
| | | generated by the trRosetta
| | | neural network be used
| | | during structure
| | | prediction? Note that
| | | this is NOT the backbone
| | | phi dihedral angle, but an
| | | inter-residue angle
| | | defined by CA1-CB1-CB2.
| | | Default true.
distance_constraint_prob_cutoff | 0.05 | R| The minimum cumulative
| | | probability for
| | | residue-pair distance
| | | constraints, below which
| | | no constraint is added.
| | | Default 0.05.
omega_constraint_prob_cutoff | 0.55 | R| The minimum cumulative
| | | probability for
| | | residue-pair omega
| | | dihedral (CA1-CB1-CB2-CA2)
| | | constraints, below which
| | | no constraint is added.
| | | Default 0.55.
theta_constraint_prob_cutoff | 0.55 | R| The minimum cumulative
| | | probability for
| | | residue-pair theta
| | | dihedral (N-CA1-CB1-CB2)
| | | constraints, below which
| | | no constraint is added.
| | | Default 0.55.
phi_constraint_prob_cutoff | 0.65 | R| The minimum cumulative
| | | probability for
| | | residue-pair phi angle
| | | (CA1-CB1-CB2) constraints,
| | | below which no constraint
| | | is added. Default 0.65.
distance_constraint_weight | 1 | R| A multiplier that can be
| | | used to alter the
| | | trRosetta distance
| | | constraint weights.
| | | Default 1.0.
omega_constraint_weight | 1 | R| A multiplier that can be
| | | used to alter the
| | | trRosetta omega constraint
| | | weights. (Note that omega
| | | is the CA1-CB1-CB2-CA2
| | | dihedral angle, not the
| | | usual backbone diheral
| | | angle.) Default 1.0.
theta_constraint_weight | 1 | R| A multiplier that can be
| | | used to alter the
| | | trRosetta theta constraint
| | | weights. Theta
| | | constraints the
| | | N1-CA1-CB1-CB2 dihedral.
| | | Default 1.0.
phi_constraint_weight | 1 | R| A multiplier that can be
| | | used to alter the
| | | trRosetta phi (angle)
| | | constraint weights. (Note
| | | that phi is the
| | | CA1-CB1-CB2 angle, not the
| | | usual backbone dihedral
| | | angle.) Default 1.0.
write_constraints_to_file | | S| If provided, trRosetta
| | | constraints are written to
| | | the specified filename.
| | | No write occurs if not
| | | provided or if set to an
| | | empty string.
only_write_constraints | false | B| If true, the the
| | | trRosettaProtocolMover or
| | | trRosetta application
| | | skips the structue
| | | prediction phase, and ONLY
| | | writes constraints to a
| | | file. Must be used in
| | | conjunction with a
| | | filename specified with
| | | the -trRosett
| | | a
| | | :write_constraints_to_file
| | | option. False by default.
backbone_randomization_mode | classic | S| The manner in which the
| | | polypeptide backbone is
| | | initially randomized. Can
| | | be 'classic' (the manner
| | | of the original Yang et
| | | al. paper), 'ramachandran'
| | | (randomizing biased by the
| | | Ramachandran preferences
| | | of each residue, or 'bins'
| | | (randomizing biased by the
| | | probability of seeing
| | | residue type i in backbone
| | | bin X and residue type i+1
| | | in backbone bin Y).
| | | Default 'classic'.
backbone_minimization_mode | classic2 | S| The protocol to use for
| | | minimizing the backbone
| | | given the constraints.
| | | Options are: 'classic0'
| | | (minimize using
| | | short-range constraints,
| | | then minimize using
| | | medium-range constraints,
| | | then minimize using
| | | long-range constraints),
| | | 'classic1' (minimize using
| | | short- and medium-range
| | | constraints, then minimize
| | | using long-range
| | | constraints), or
| | | 'classic2' (minimize using
| | | all constraints).
| | | Defaults to 'classic2'.
cis_peptide_prob_non_prepro | 0.0005 | R| The probability of sampling
| | | a cis peptide bond at
| | | positions that do not
| | | precede proline. Note
| | | that cis omega sampling
| | | only happens in
| | | 'ramachandran' backbone
| | | randomization mode, not in
| | | 'classic'. (In 'bins'
| | | mode, the bin transition
| | | probabilities govern cis
| | | sampling.) Defaults to
| | | 0.0005; must be a value
| | | from 0.0 to 1.0.
cis_peptide_prob_prepro | 0.05 | R| The probability of sampling
| | | a cis peptide bond at
| | | positions that precede
| | | proline. Note that cis
| | | omega sampling only
| | | happens in 'ramachandran'
| | | backbone randomization
| | | mode, not in 'classic'.
| | | (In 'bins' mode, the bin
| | | transition probabilities
| | | govern cis sampling.)
| | | Defaults to 0.05; must be
| | | a value from 0.0 to 1.0.
scorefxn0 | trRosetta_cen0.wts | F| Weights file for
| | | scorefunction used during
| | | initial (stage 0)
| | | minimization by the
| | | trRosettaProtocol mover.
| | | Defaults to
| | | trRosetta_cen0.wts.
scorefxn1 | trRosetta_cen1.wts | F| Weights file for
| | | scorefunction used during
| | | stage 1 minimization by
| | | the trRosettaProtocol
| | | mover. Defaults to
| | | trRosetta_cen0.wts.
scorefxn2 | trRosetta_cen2.wts | F| Weights file for
| | | scorefunction used during
| | | clash relief (stage 2 --
| | | Van der Waals stage)
| | | minimization by the
| | | trRosettaProtocol mover.
| | | Defaults to
| | | trRosetta_cen0.wts.
scorefxn3 | trRosetta_cart.wts | F| Weights file for
| | | scorefunction used during
| | | late-stage (stage 3 --
| | | Cartesian stage)
| | | minimization by the
| | | trRosettaProtocol mover.
| | | Defaults to
| | | trRosetta_cen0.wts.
scorefxn_fullatom | | F| Weights file for
| | | scorefunction used for
| | | fullatom refinement with
| | | FastRelax. If
| | | atom-pair_constraint,
| | | dihedral_constraint, or
| | | angle_constraint terms are
| | | zero, they will be set to
| | | 5.0, 1.0, and 1.0
| | | respectively. If empty
| | | (the default), then the
| | | scoring function specified
| | | with -score:weights is
| | | used instead.
mutate_gly_to_ala | | B| If true, glycine residues
| | | are mutated to alanine
| | | during the centroid phase
| | | of minimization, then
| | | converted back for
| | | fullatom refinement. True
| | | by default to match the
| | | original PyRosetta
| | | protocol.
fullatom_refinement | | B| If true, the structure is
| | | converted to a fullatom
| | | structure and the
| | | FastRelax protocol is run
| | | at the end. The energy
| | | function used for this
| | | step is the Rosetta
| | | default energy function
| | | (with atom-pair, dihedral,
| | | and angle constraint terms
| | | turned on if they are
| | | not). This can be set
| | | with the -
| | | t
| | | rRosetta:scorefxn_fullatom
| | | flag. True by default.Recommended flags
At the time of this writing, the recommended best practice flags are:
-mutate_gly_to_ala false
-backbone_randomization_mode ramachandranThese may become default at some point in the future. All other settings may be left in their default values.
Limitations
- The trRosetta neural network is trained on hundreds of millions of known sequences and hundreds of thousands of known structures. Proteins with few close homologues or with unusual sequences or backbone geometry may be predicted poorly.
- The models produced tend to have limited diversity. The trRosetta minimization protocol is a good one for predicting the native state of a well-folded protein, but may not be the best for conformational sampling the energy landscape of a sequence. For that, consider using the AbinitioRelax application, with or without the
-use_trRosetta_constraintsoption, to carry out fragment insertion-based conformational sampling. - The trRosetta protocol can currently only be used on single-chain poses composed entirely of canonical amino acids. Cofactors, posttranslational modifications, multi-chain proteins, and noncanonical building blocks are currently unsupported.
- This protocol is intended for soluble proteins. Support for membrane proteins is planned.
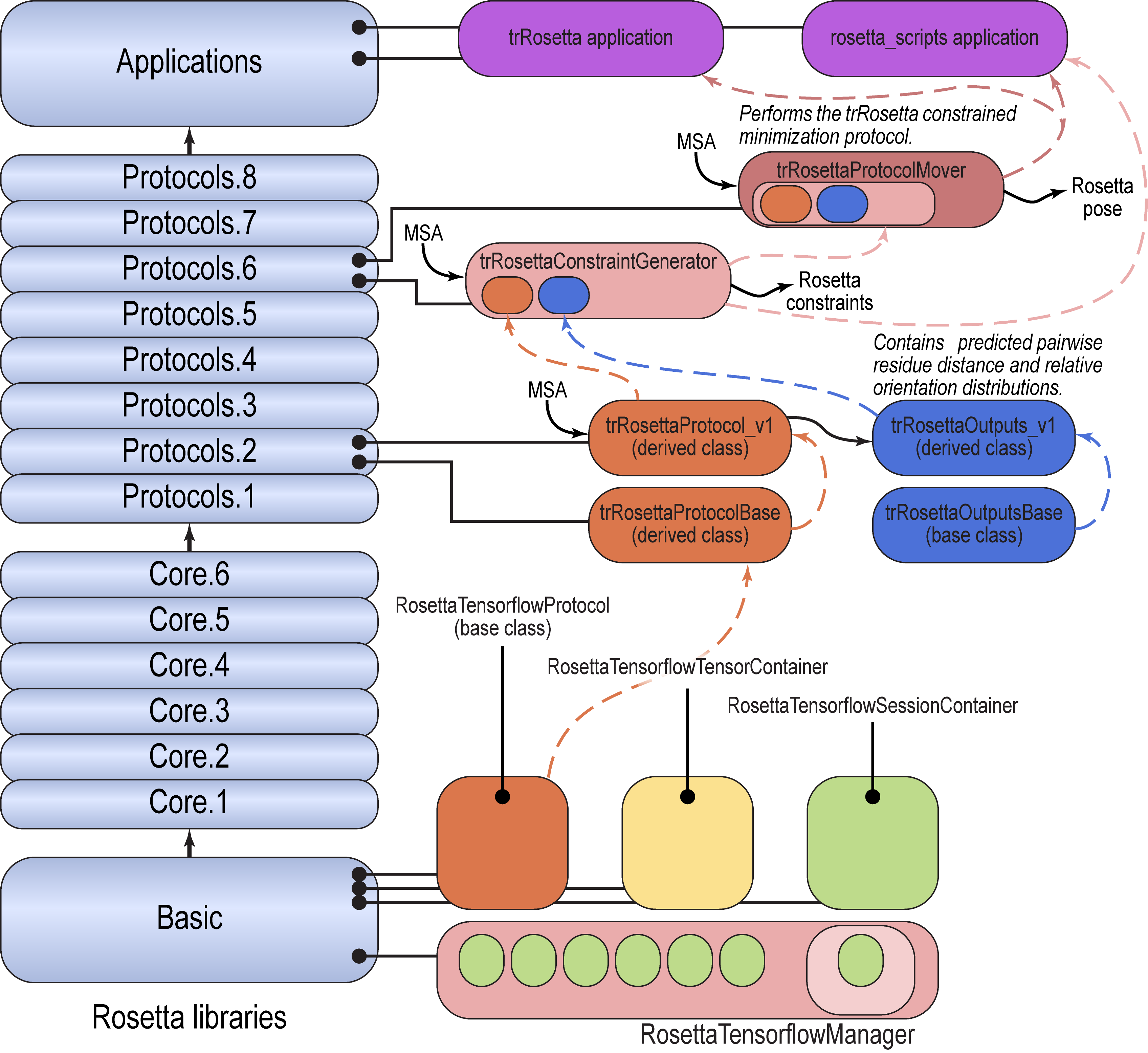
Code Organization
- The trRosetta neural network parameters are located in the Rosetta database, in
Rosetta/main/database/protocol_data/tensorflow_graphs/tensorflow_graph_repo_submodule/trRosetta/model_v1/. - The
RosettaTensorflowManager, low-level code for loading Tensorflow models and using them in Rosetta protocols is located inRosetta/main/source/src/basic/tensorflow_manager. - The code to convert a multiple sequence alignment to a one-hot 3D tensor, to run the trRosetta neural network, and to store the results in an output object containing distance, omega, theta, and phi tensors is located in
Rosetta/main/source/src/protocols/trRosetta/. ThetrRosettaProtocolBaseandtrRosettaOutputsBaseclasses are abstract base classes, and thetrRosettaProtocol_v1andtrRosettaOutputs_v1derived classes implement the process of converting inputs to tensors, running the network, and producing outputs, and provide a place to store outputs, respectively. - The trRosettaConstraintGenerator converts
trRosettaOutputs_v1into Rosetta constraints. It contains thetrRosettaProtocol_v1internally, and runs it to generate the outputs. It is located inRosetta/main/source/src/protocols/trRosetta_protocols/constraint_generators/. - The full protocol to take an MSA and produce a predicted pose is implemented as the trRosettaProtocol mover, located in
Rosetta/main/source/src/protocols/trRosetta_protocols/movers. This mover encapsulates the trRosettaConstraintGenerator, which in turn encapsulates thetrRosettaProtocol_v1class. - The trRosetta application is implemented in
Rosetta/main/source/src/apps/public/trRosetta/trRosetta.cc. - The code is intended to be modular and extensible as new versions of the trRosetta neural network become available.
References
- The trRosetta neural network is described in Yang et al. (2020) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117(3):1496-1503 (doi 10.1073/pnas.1914677117).
- The trRosettaProtocol mover, trRosettaConstraintGenerator, trRosetta application, and other C++ infrastructure were written by Vikram K. Mulligan (vmulligan@flatironinstitute.org), and are currently unpublished.
History
- The trRosetta neural network was developed by Jianyi Yang, Ivan Anishchenko, and Sergey Ovchinnikov in 2019.
- A PyRosetta-based protocol was developed for use in the 2020 CASP14 protein structure prediction competition. This protocol converted trRosetta generated distance and inter-reside orientation probability distributions into Rosetta constraints, applied them to a pose, and used constrained minimization to generate the final structure (followed by all-atom relaxation with the FastRelax protocol.
- The C++ implementation was written in Jan-Mar 2021 by Vikram K. Mulligan, Flatiron Institute.
Differences from original Python version
- The original PyRosetta implementation mutated all glycine residues to alanine during centroid phases of the protocol, and back again during the full-atom phase. This allowed the CA1-CB1-CB2-CA2 dihedral to be defined even for glycine residues during centroid minimization, but during full-atom minimization, glycine orientation constraints were ignored. The C++ implementation follows nearly the same protocol, with two exceptions:
- Although glycine residues are by default temporarily mutated to alanine during the centroid phase, and then reverted to glycine for full-atom refinement, as in the Python protocol, if this is overridden with the
-mutate_gly_to_ala falseoption, the C++ code uses the CEN atom in place of CB for glycine residues when constraining dihedrals in centroid mode. - In fullatom mode, the C++ code uses 1HA in place of CB for glycine residues when constraining dihedrals. This means that orientation constraints for glycine are not ignored in fullatom refinement phases.
- Although glycine residues are by default temporarily mutated to alanine during the centroid phase, and then reverted to glycine for full-atom refinement, as in the Python protocol, if this is overridden with the
- In "ramachandran" or "bins" initialization modes, cis peptide bonds are sampled.
See Also
- Structure prediction applications: Includes links to these and other applications for loop modeling
- RosettaScripts: The RosettaScripts home page
- Application Documentation: List of Rosetta applications
- AbinitioRelax application: The Rosetta ab intio fragment-based structure prediction application.
- Running Rosetta with options: Instructions for running Rosetta executables.
- Comparing structures: Essay on comparing structures
- Analyzing Results: Tips for analyzing results generated using Rosetta
- Solving a Biological Problem: Guide to approaching biological problems using Rosetta
- Commands collection: A list of example command lines for running Rosetta executable files